CURRENT AFFAIRS
9-10 NOVEMBER 2019
1.SC's verdict on Ayodhya(gs-1,2)
- Context:SC's verdict on Ayodhya issue widely welcomed across country, abroad
- Understanding the history of the case…….articles compilation related to Ayodhya case……
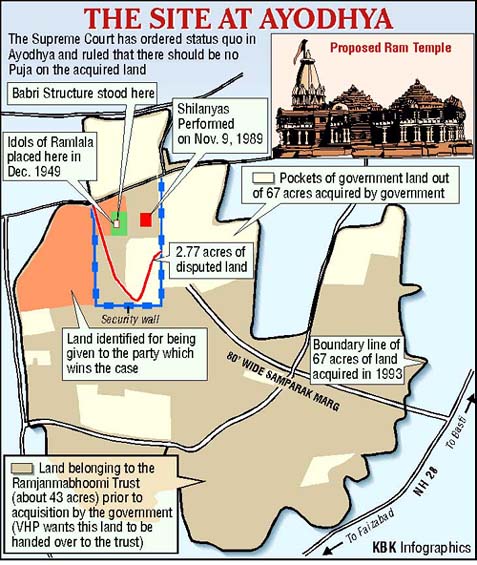
- The Supreme Court verdict in the Ayodhya land dispute case has been widely welcomed across the country and abroad. In a historic unanimous decision, a five-judge Constitution bench headed by Chief Justice of India Ranjan Gogoi yesterday ruled that the entire 2.77 acres of the disputed land in Ayodhya will remain with the Central government and be handed over to a Trust for the construction of a temple. The bench also ruled that a suitable five-acre plot must be found for a mosque at a prominent place in the town.
- Addressing the nation last evening, Prime Minister Narendra Modi said, the apex court's ruling adds a golden chapter in India’s judiciary. Lok Sabha Speaker Om Birla said, the verdict will further strengthen the confidence of the people in the country's judicial system. In a series of tweets, Home Minister Amit Shah said, the order will prove to be a milestone and further strengthen India's unity and integrity.
Understanding the history of the case…….articles compilation related to Ayodhya case……
What was the Ayodhya Dispute?
- Lord Ram, one of the most revered gods in Hinduism, was born in Ayodhya and later ruled over his kingdom from here.
- A temple is said to be built in the early medieval ages to commemorate his birth place (Janmabhoomi)
- 1528 – A mosque was built, purportedly at the same site by destroying the Janmabhoomi temple, by Mir Baqi – a general of Babur The political, historical and socio-religious debate over the history of the site and whether a previous temple was demolished or modified to create the mosque, is known as the Ayodhya dispute.
Beginning of the Dispute
- For centuries, Muslims prayed inside the mosque while Hindus continued worshipping the Janmabhoomi, just outside on a chabutra (raised platform)
- 1853 – Local Rioting and clashes for control over Mosque
- 1885 – Mahant Raghuvar Das pleaded in Faizabad court to build a temple over Ram Chabutra (a platform) near the masjid . The request was denied
- Rekindling of the dispute – Events of 1949
- 22/23 December 1949 – ‘’Appearance’’ of Ramlala (infant Lord Ram) idol inside the mosque premises
- The D.M., KK Nair took control of premises when local Muslims complained about the placement of idols.
- January 1950 – Mahant Ramchandra Das appealed the court to allow prayers inside the structure
- Court decreed that prayers will be from outside – no entry inside the structure to public (Hindu or Muslim) . The premises were henceforth locked by administration
- 1959 – Nirmohi Akhara filed another case asking for control of the site from the administration
- 1961- The Sunni Waqf board went to court asking for removal of idols, stopping Hindu prayers at the site and giving control of the site to Waqf board
- * Waqf is a permanent dedication of movable or immovable properties for religious or charitable purposes
The Politics of 1980s
- 1984 – Dharma Sansad (conclave) by Vishwa Hindu Parsihad Ram Mandir issue comes to the forefront of national politics
- 1986 – Shah Bano case Opening of the premises for Hindu worship – TV broadcast on DD Appeasement?
- Protests by Muslims at many places
- Babari masjid action committee (BMAC) formed
- ‘Hindutva’ politics – VHP, along with Sangh parivar affiliates and Hindu nationalist political party BJP started a socio religious as well as political campaign to construct a temple at the Janmabhoomi site
- Karseva – voluntary service for temple work • Organisation of Ram Janaki Rathyatra in Ayodhya
- Bajrang Dal was formed – youth wing of VHP
- Shila poojan – bricks collected from all over the country for temple construction
- August 1989 – the Lucknow bench of the Allahabad High Court bunched together all the petitions regarding the dispute over Babari Masjid site and ordered that status quo be maintained.
- November 1989 – ‘Shilanyas’ Stone-laying ceremony performed by VHP near the disputed site
- Riots in multiple cities – 1000 dead
- General elections in December 1989 – Congress/Rajiv Gandhi lost the mandate
- VP Singh leading the National Front, became Prime Minister with outside support of right wing BJP (85 Seats) as well as the left parties.
- Rath Yatra by Advani 25 Sept – 30 Oct 1990
- BJP president LK Advani toured the northern states on a rath – a bus converted to look like a mythical chariot – with the intention of drumming up support for Ram Mandir.
- 10,000 Km – from Somnath in Gujarat to Ayodhya, UP
- Bloody trail of rath – riots along the path of Yatra
- 23 Oct 1990 – Advani was arrested in Samastipur, Bihar BJP pulled support to VP singh Government in centre Chandrashekhar became Prime Minister with support of Congress
- Attempts to bring down the masjid by Karsevaks on 30 October 1990 – failed
- 1991- Rajiv Gandhi assassinated while campaigning for elections
- Congress returned to power – Prime Minister – PV Narsimha Rao BJP stormed to power in UP assembly elections with 221/425 seats Chief Minister – Kalyan singh
- The new Govt acquired 2.77 acre of the disputed site for tourism purposes and leased it to the Janmabhoomi Nyas (trust)
- Meanwhile the Allahabad High court banned any permanent construction on the disputed site.
- Kalyan singh govt submitted to the court that it will maintain status quo and not allow any construction on the site.
- July 1992- Karsevaks started construction of a platform on the disputed site
- Tensions between state and centre governments
- PV Narsimha Rao tries to mediate and solve the dispute – VHP and Babari Masjid Action Committee started talks to resolve the dispute out of court for the first time ever Talks failed
- 30 October 1992- VHP Dharm Sansad announced 6th December as day of ‘Karseva’
The Demolition of Babari Masjid
- In late November 1992, Kalyan singh assured centre that no construction will be allowed on the site (acc to court orders)
- He also announced publicly that no ‘Karsevak’ would be fired upon and that police have been given such instructions
- Karseva day on 6th December 1992
- ~2 lakh crowd gathered in Ayodhya
- Ashok Singhal, LK Advani, Murli Manohar Joshi, Uma Bharti and other senior BJP/VHP leaders were present at the site (few hundred metres away) giving speeches.
- With whatever tools and instruments they could lay their hands on , Karsevaks climbed up the Babari masjid structure and brought it down by late afternoon.
- A rudimentary temple site with Ramlala idol was set up by evening
- CM Kalyan Singh resigned the same day
Ensuing Riots
- Riots started across India soon after the Babari masjid was demolished
- Riots were severe in Bombay* – 800-1000 died
- More than 2000 people died all over the country
- Anti Hindu riots + destruction of many temples in Pakistan and Bangladesh
- 1993 serial blasts in Bombay – perceived as retaliation for Babari masjid demolition
Liberhan Commission
- 48 extensions and 17 years time
- Report tabled – June 2009
- The report holds 68 people culpable, including L K Advani, Murli Manohar Joshi, Atal Bihari Vajpayee and more critically, Kalyan Singh
- The report accused the RSS + VHP of being the chief architect of the demolition
- The report was labelled ‘politically motivated’ by BJP,VHP and RSS
ASI excavations
- 2003 – High Court ordered Archaeological Survey of India to carry out excavations at the disputed site in Ayodhya
- The ASI report stated that multiple structures – especially pillars showing Hindu motifs, point to a large Hindu complex predating the mosque (10/11th century)
- ASI called it a ‘shrine’
- Difference of interpretation on the findings – debated among Historians
- 19th century excavations by ASI reported Buddhist era structures
- Pro Temple arguments: Archaeological evidence – pointing to a temple complex
- Accounts of some European travellers during Mughal period state that
- a temple was destroyed to build a Mosque (Masjid-e-Janamsthan) Hindus worshipping Ram lalla just outside the Mosque since centuries
- Question of honouring the belief and sentiments of a billion Hindus
Pro Mosque arguments: ASI report is inconclusive
- Ramcharitmanas (1576) does not mention any destruction of temple
- at Janmabhoomi The mosque stood for 460 years – a very long time.
- It was a historical building and an important site of worship for
- Muslims – question of faith of millions of Muslims in India How far back will one go to rectify historical events?
The legal case(earlier)
- The multiple cases were clubbed together by Allahabad High court.
- Verdict of High court on 30 September 2010
- Three way division of disputed site between – 1. Ram Lalla (Ram Janmabhoomi nyas) – central shrine where idol is placed 2. Nirmohi Akhara – Sita rasoi and Ram Chabutra (peripheral structures) 3. Sunni Waqf board – Rest For the first time in a judicial ruling, court accepted that the disputed site was the birthplace of Lord Ram
- None of the parties were satisfied by the verdict and all of them appealed in the Supreme Court
- SC hearing to begin – August 2017
- Deferred to December 2017
- Meanwhile CBI has brought about criminal conspiracy charges against L.K. Advani, Uma Bharti and Murli Manohar Joshi (VHP leaders Ashok Singhal and Giriraj Kishore – died pending trial)
Continued earlier Importance(but this has changed now due to yestrerdays verdict)
- The dispute posed a challenge to India’s unity, social fabric and law and order situation for many years
- Many terrorist groups have cited the demolition in 1992 as the cause for terrorist attacks on Indian cities
- India’s secular image and respect for the rule of law took a body blow on world stage after 1992
- The Godhra riots of 2002 began after torching of 60 Karsevaks enroute Ayodhya.
- The boundaries of Politics and Religion have blurred
some earlier news articles:::


yesterdays final verdict:

2.Kartarpur Corridor(gs-1.2)
- Context:Kartarpur Corridor gets the thumbs-up from Indian pilgrims
- KARTARPUR SAHIB: The opening of the Kartarpur Corridor on the Pakistan side turned out to be lively, colourful ceremony with the first jatha of Indian pilgrims comprising, among others, former PM Manmohan Singh and union ministers Hardeep Puri and Harsimrat Badal speaking in glowing terms about the corridor. While Manmohan, accompanied by his wife Gursharan Kaur, said it was a good thing for both countries that the corridor had opened after a wait of over 70 years, Harsimrat said those talking about the possible use of corridor to revive the Khalistan movement did not believe in Guru Nanak or his teachings.
Kartarpur Corridor:
- India and Pakistan have signed an agreement to operationalise the Kartarpur corridor. The agreement is valid initially for five years.
- Either party can terminate the agreement at any time by giving notice of one month to the other party of its intention to terminate this agreement.
- Also, the pact could be suspended in case of exigency or persistent violation of its provisions.
- The Pakistan side has agreed to make sufficient provision for langar and distribution of prasad in the Gurdwara premises.
- On Indian side, all the required infrastructure, including the highway and the passenger terminal building are near completion for timely inauguration of the corridor.
- The corridor is expected to be inaugurated on 9th November 2019.
- It would remain open throughout the year.
Kartarpur Corridor

- The Kartarpur corridor connects the Darbar Sahib Gurdwara in Narowal district of Pakistan with the Dera Baba Nanak shrine in Gurdaspur district in India’s Punjab province.
- The agreement will facilitate visa-free movement of Indian pilgrims who would just need a permit to cross over to Pakistan.
- The corridor was built to commemorate 550th birth anniversary celebrations of Guru Nanak Dev, founder of Sikhism on 12th November 2019.
Guru Nanak:
- Guru Nanak Dev Jayanti is observed on the full-moon day in the month of Katak to celebrate the birth of Guru Nanak Dev (1469-1539).
- He advocated the 'Nirguna' form of bhakti. He rejected sacrifices, ritual baths, image worship, austerities and the scriptures of both Hindus and Muslims.
- He set up rules for congregational worship (sangat) involving collective recitation.
- He appointed one of his disciples, Angad, to succeed him as the preceptor (guru), and this practice was followed for nearly 200 years.
- The fifth preceptor, Guru Arjan, compiled Baba Guru Nanak’s hymns along with those of his four successors and also other religious poets, like Baba Farid, Ravidas (also known as Raidas) and Kabir, in the Adi Granth Sahib.
- These hymns, called 'Gurbani', are composed in many languages.
- Kartarpur gurudwara is the revered shrine about 4km across the border where Guru Nanak Dev spent the last 18 years of his life.
3.Uranium enrichment, Iran nuclear deal(gs-2,3)
- context:Iran says enriching uranium to five percent
- Iran today said that it is now enriching uranium to five percent, after stepping back from its commitments under the troubled 2015 accord with significant powers.
- The deal four years ago set a 3.67 percent limit for uranium enrichment, but Tehran announced it would no longer respect it after the United States unilaterally abandoned the agreement last year and reimposed crippling sanctions
Iran nuclear deal: Key details:::
- In 2015, Iran agreed a long-term deal on its nuclear programme with a group of world powers known as the P5+1 - the US, UK, France, China, Russia and Germany.
- It came after years of tension over Iran's alleged efforts to develop a nuclear weapon. Iran insisted that its nuclear programme was entirely peaceful, but the international community did not believe that.
- Under the accord, Iran agreed to limit its sensitive nuclear activities and allow in international inspectors in return for the lifting of crippling economic sanctions.
Uranium enrichment:
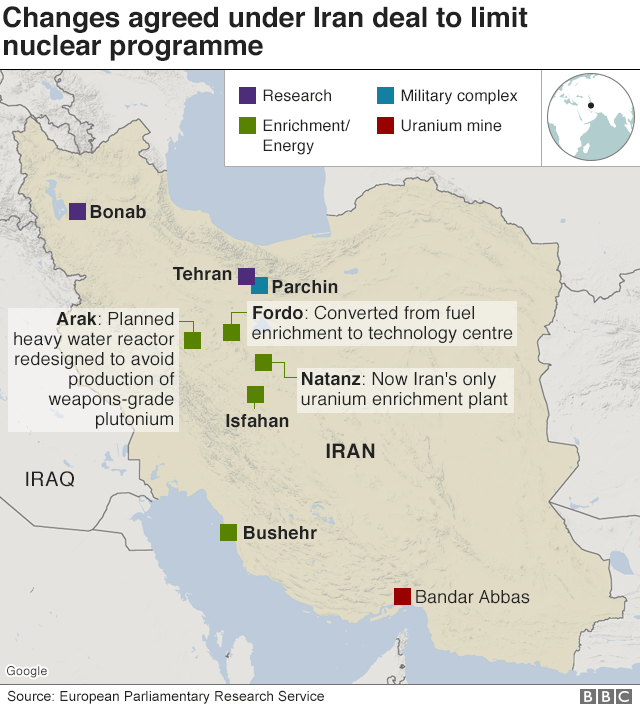
- Iran had two facilities - Natanz and Fordo - where uranium hexafluoride gas was fed into centrifuges to separate out the most fissile isotope, U-235.
- Low-enriched uranium, which has a 3%-4% concentration of U-235, can be used to produce fuel for nuclear power plants. "Weapons-grade" uranium is 90% enriched.
- In July 2015, Iran had almost 20,000 centrifuges. Under the JCPOA, it was limited to installing no more than 5,060 of the oldest and least efficient centrifuges at Natanz until 2026 - 10 years after the deal's "implementation day" in January 2016.
- Iran's uranium stockpile was reduced by 98% to 300kg (660lbs), a figure that must not be exceeded until 2031. It must also keep the stockpile's level of enrichment at 3.67%.
- By January 2016, Iran had drastically reduced the number of centrifuges installed at Natanz and Fordo, and shipped tonnes of low-enriched uranium to Russia.
- In addition, research and development must take place only at Natanz and be limited until 2024.
- No enrichment will be permitted at Fordo until 2031, and the underground facility will be converted into a nuclear, physics and technology centre. The 1,044 centrifuges at the site will produce radioisotopes for use in medicine, agriculture, industry and science.
4.Indra-2019 (gs-2)
- Context:India-Russia tri-service exercise next month
- Mechanised contingents, fighter and transport aircraft as well ships of the armed forces of India and Russia will be part of the joint tri-service exercise Indra-2019 scheduled next month, sources said on Saturday.
- In preparation of the exercise, a joint planning conference is being held from November 7 to 10 in two phases.
- Phase one of the conference was conducted on November 7 and 8 at respective service locations of Babina, Pune and Goa to discuss service specific modalities.
Indra-2019 
- India and Russia will hold the eleventh iteration of their bilateral military exercise, designated Indra-2019, in December of this year. The exercise will principally take place at a training ground in India. According to the press office of Russia’s Eastern Military District cited in a TASS news agency report, Indra-2019 will involve eight tactical episodes involving the ground forces of both countries.
- “At the first conference for planning, which came to an end in the city of Ussuriysk (the Primorye Region), representatives of the command of the Eastern Military District and the Armed Forces of the Republic of India agreed the goals of the upcoming Indra-2019 Russian-Indian joint military exercise,” the press release notes.
- “The sides agreed that the drills would practice the issues of training military command centers in exercising command and control of all-arms forces for solving joint tasks… About eight tactical episodes have been mapped out for the ground-based grouping of forces,” it added.
- Other parts of the exercise, including air and naval drills, will also take place on Indian territory.
- The Russian military is expected to dispatch around 300 ground troops from motorized infantry units. It has not revealed yet what and how may aircraft and warships will participate in the exercise.
- The Indian Ministry of Defense (MoD) has so far not announced any troop numbers or other military assets to take part in the Indo-Russian drills.
- In 2018, land component of the exercise took place at India’s Babina Military Station, near Jhansi in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It reportedly involved 14 T-90 tanks, 14 BMP-2 infantry fighting vehicles, and 500 troops on the Russian side, according to the Russian MoD, while India did not reveal the assets involved.
- “The aim of the exercise is to practice joint planning and conduct to enhance interoperability of the two armies in the peace keeping and enforcement environment under the aegis of United Nations,” an Indian Ministry of Defense statement noted at the time.
- The naval part of the exercise, dubbed Indra Navy, took place in the Bay of Bengal last year. The Indian Navy dispatched the “INS Ranvir, a guided missile destroyer, INS Satpura, an indigenous frigate, INS Kadmatt, an indigenous anti- submarine warfare (ASW) corvette, IN Ships Kuthar and Khanjarboth indigenous missile corvettes and INS Jyoti, a fleet tanker” to the exercise, according to an Indian MoD press release.
- The Russian Navy in turn, sent the flagship of its Pacific Fleet, the Slava-class guided missile cruiser, Varyag, as well as the Admiral Panteleyev, an Udaloy-class anti-submarine warfare ship, and the sea tanker, Boris Butoma. The principal aim of the naval exercise was to increase interoperability amongst the two navies.
5.NATO(gs-2,3)
- Context:Trump to host NATO chief as alliance faces strains
- U.S. President Donald Trump will host NATO chief Jens Stoltenberg in Washington at a time of severe strain within the Atlantic alliance, the White House announced on November 9.
- The two leaders will discuss allies' NATO "progress on increasing defense spending and ensuring more equitable burden-sharing," the White House statement said.
NATO :
- North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO)
- The North Atlantic Treaty Organisation (NATO), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, the Atlantic Alliance or the Western Alliance, is an international organisation for collective security established in 1949, in support of the North Atlantic Treaty signed in Washington, DC, on 4 April 1949. Its headquarters are located in Brussels, Belgium. Its other official name is the French equivalent, l’Organisation du Traité de l’Atlantique Nord (OTAN) (English and French being the two official languages of the organisation).
Background
- The Treaty of Brussels, signed on 17 March 1948 by Belgium, the Netherlands, Luxembourg, France, and the United Kingdom, is considered the precursor to the NATO agreement. This treaty established a military alliance, later to become the Western European Union. However, American participation was thought necessary in order to counter the military power of the Soviet Union, and therefore talks for a new military alliance began almost immediately. These talks resulted in the North Atlantic Treaty, which was signed in Washington, DC on 4 April 1949.
- It included the five Treaty of Brussels states, United States, Canada, Portugal, Italy, Norway, Denmark and Iceland. Three years later, on 18 February 1952, Greece and Turkey also joined. Because of geography, Australia and New Zealand missed out on membership.
- In place of this, the ANZUS agreement was made by the United States with these nations. The incorporation of West Germany into the organisation on 9 May 1955 was described as “a decisive turning point in the history of our continent” by Halvard Lange, Foreign Minister of Norway at the time.
- Indeed, one of its immediate results was the creation of the Warsaw Pact, signed on 14 May 1955 by the Soviet Union and its satellite states as a formal response to this event, firmly establishing the two opposing sides of the Cold War.
Détente
- During most of the duration of the Cold War, NATO maintained a holding pattern with no actual military engagement as an organisation. On 1 July 1968, the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty opened for signature: NATO argued that its nuclear weapons sharing arrangements did not breach the treaty as US forces controlled the weapons until a decision was made to go to war, at which point the treaty would no longer be controlling. Few states knew of the NATO nuclear sharing arrangements at that time, and they were not challenged. On 30 May 1978, NATO countries officially defined two complementary aims of the Alliance, to maintain security and pursue détente. This was supposed to mean matching defences at the level rendered necessary by the Warsaw Pact’s offensive capabilities without spurring a further arms race. However, on 12 December 1979, in light of a build-up of Warsaw Pact nuclear capabilities in Europe, ministers approved the deployment of US Cruise and Pershing II theatre nuclear weapons in Europe.
- The new warheads were also meant to strengthen the western negotiating position in regard to nuclear disarmament. This policy was called the Dual Track policy. Similarly, in 1983–84, responding to the stationing of Warsaw Pact SS-20 medium-range missiles in Europe, NATO deployed modern Pershing II missiles able to reach Moscow within minutes. This action led to peace movement protests throughout Western Europe.
- The membership of the organisation in this time period likewise remained largely static, with NATO only gaining one new member in 30 May 1982, when newly democratic Spain joined the alliance, following a referendum.
- Greece also in 1974 withdrew its forces from NATO’s military command structure, as a result of Greco-Turkish tensions following the 1974 Cyprus dispute; Greek forces were however readmitted in 1980. In November 1983, a NATO manoeuvre code-named Able Archer 83, which simulated a NATO nuclear release, caused panic in the Kremlin. Soviet leadership, led by ailing General Secretary Yuri Andropov became concerned that US President Ronald Reagan may have been intending to launch a genuine first strike.
- In response, Soviet nuclear forces were readied and air units in Eastern Germany and Poland were placed on alert. Though at the time written off by US intelligence as a propaganda effort, many historians now believe Soviet fear of a NATO first strike was genuine.
Post-Cold War
- The end of the Cold War, the dissolution of the Warsaw Pact in 1991, removed the de facto main adversary of NATO. This caused a strategic reevalution of NATO’s purpose, nature and tasks. In practice this ended up entailing a gradual (and still ongoing) expansion of NATO to Eastern Europe, as well as the extension of its activities to areas not formerly concerning it.
- The first post-Cold War expansion of NATO came with the reunification of Germany on 3 October 1990, when the former East Germany became part of the Federal Republic of Germany and the alliance. This had been agreed in the Two Plus Four Treaty earlier in the year..
- To secure Soviet approval of a united Germany remaining in NATO, it was agreed that foreign troops and nuclear weapons would not be stationed in the east, and also that NATO would never expand further east. On 28 February 1994, NATO also took its first military action, shooting down four Bosnian Serb aircraft violating a UN no-fly zone over central Bosnia and Herzegovina.
- NATO air strikes the following year help bring the war in Bosnia to an end, resulting in the Dayton Agreement. Between 1994 and 1997, wider forums for regional cooperation between NATO and its neighbours were set up, like the Partnership for Peace, the Mediterranean Dialogue initiative and the Euro-Atlantic Partnership Council. On 8 July 1997, three former communist countries, Hungary, the Czech Republic, and Poland, were invited to join NATO, which finally happened in 1999.
- On 24 March 1999, NATO saw its first broad-scale military engagement in the Kosovo War, where it waged an 11-week bombing campaign against what was then the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. The conflict ended on 11 June 1999, when Yugoslavian leader Slobodan Milošević agreed to NATO’s demands by accepting UN resolution 1244. NATO then helped establish the KFOR, a NATO-led force under a United Nations mandate that operates the military mission in Kosovo. Debate concerning NATO’s role and the concerns of the wider international community continued throughout its expanded military activities:
- The United States opposed efforts to require the UN Security Council to approve NATO military strikes, such as the ongoing action against Yugoslavia, while France and other NATO countries claimed the alliance needed UN approval. American officials said that this would undermine the authority of the alliance, and they noted that Russia and China would have exercised their Security Council vetoes to block the strike on Yugoslavia.
- In April 1999, at the Washington summit, a German proposal that NATO adopt a no-first-use nuclear strategy was rejected.
After the September 11th attacks
- The expansion of the activities and geographical reach of NATO grew even further as an outcome of the September 11th attacks. These caused as a response the provisional invocation (on September 12) of the collective security of NATO’s charter — Article 5 which states that any attack on a member state will be considered an attack against the entire group of members. The invocation was confirmed on 4 October 2001 when NATO determined that the attacks were indeed eligible under the terms of the North Atlantic Treaty.
- The eight official actions taken by NATO in response to the attacks included the first two examples of military action taken in response to an invocation of Article 5: Operation Eagle Assist and Operation Active Endeavour. Despite this early show of solidarity, NATO faced a crisis little more than a year later, when on 10 February 2003, France and Belgium vetoed the procedure of silent approval concerning the timing of protective measures for Turkey in case of a possible war with Iraq. Germany did not use its right to break the procedure but said it supported the veto. On the issue of Afghanistan on the other hand, the alliance showed greater unity: On 16 April 2003 NATO agreed to take command of the International Security Assistance Force (ISAF) in Afghanistan.
- The decision came at the request of Germany and the Netherlands, the two nations leading ISAF at the time of the agreement, and all 19 NATO ambassadors approved it unanimously. The handover of control to NATO took place on 11 August, and marked the first time in NATO’s history that it took charge of a mission outside the north Atlantic area. Canada had originally been slated to take over ISAF by itself on that date.
Political Structure
- Like any alliance, NATO is ultimately governed by its 26 member states. However, the North Atlantic Treaty, and other agreements, outline how decisions are to be made within NATO. Each of the 26 members sends a delegation or mission to NATO’s headquarters in Brussels, Belgium. The senior permanent member of each delegation is known as the Permanent Representative and is generally a senior civil servant or an experienced ambassador (and holding that diplomatic rank).
- Together the Permanent Members form the North Atlantic Council (NAC), a body which meets together at least once a week and has effective political authority and powers of decision in NATO. From time to time the Council also meets at higher levels involving Foreign Ministers, Defence Ministers or Heads of Government and it is at these meetings that major decisions regarding NATO’s policies are generally taken. However, it is worth noting that the Council has the same authority and powers of decision-making, and its decisions have the same status and validity, at whatever level it meets.
- The meetings of the North Atlantic Council are chaired by the Secretary General of NATO and, when decisions have to be made, action is agreed upon on the basis of unanimity and common accord. There is no voting or decision by majority. Each nation represented at the Council table or on any of its subordinate committees retains complete sovereignty and responsibility for its own decisions. The second pivotal member of each country’s delegation is the Military Representive, a senior officer from each country’s armed forces. Together the Military Representatives form the Military Committee, a body responsible for recommending to NATO’s political authorities those measures considered necessary for the common defence of the NATO area. Its principal role is to provide direction and advice on military policy and strategy.
- It provides guidance on military matters to the NATO Strategic Commanders, whose representatives attend its meetings, and is responsible for the overall conduct of the military affairs of the Alliance under the authority of the Council. Like the council, from time to time the Military Committee also meets at a higher level, namely at the level of Chiefs of defence, the most senior military officer in each nation’s armed forces. The NATO Parliamentary Assembly is made up of legislators from the member countries of the North Atlantic Alliance as well as 13 associate members.
Military structure
- NATO’s military operations are directed by two Strategic Commanders, both senior U.S. officers assisted by a staff drawn from across NATO. The Strategic Commanders are responsible to the Military Committee for the overall direction and conduct of all Alliance military matters within their areas of command.
- Before 2003 the Strategic Commanders were the Supreme Allied Commander Europe (SACEUR) and the Supreme Allied Commander Atlantic (SACLANT) but the current arrangement is to separate command responsibility between Allied Command Transformation (ACT), responsible for transformation and training of NATO forces, and Allied Command Operations, responsible for NATO operations world wide.
- The commander of Allied Command Operations retained the title “Supreme Allied Commander Europe (SACEUR)”, and is based in the Supreme Headquarters Allied Powers Europe (SHAPE) located at Casteau, north of the Belgian city of Mons. This is about 80 km (50 miles) south of NATO’s political headquarters in Brussels.
6.OPEN DEFECATION + (ODF +)
(gs-2)
- Context:National workshop on ODF Plus held with 12 States in New Delhi
- With all 5.99 lakh villages, 699 districts and 35 states and union territories having declared themselves open defecation free (ODF) under the Swachh Bharat Mission (Grameen) [SBM(G)] as of October 2019, the Department of Drinking Water and Sanitation (DDWS), Ministry of Jal Shakti organised a one-day national workshop on ODF Plus – ODF Sustainability and Solid and Liquid Waste Management on Saturday in New Delhi.
- Secretaries in-charge of rural sanitation, Mission Directors and other key state level officials from 12 states attended the workshop.
- Opening the workshop, Parameswaran Iyer, Secretary (DDWS), Ministry of Jal Shakti, shared that although tremendous progress had been made under the SBM(G), since the programme’s inception in 2014, the work is not yet over, and it is key that all stakeholders continue their efforts to sustain safe sanitation and to ensure that no one is left behind.
- States were encouraged to take stock of their rural sanitation situation and lay focus on sustaining the gains made under the SBM(G) and ensuring general cleanliness in the villages with solid and liquid waste management (SLWM).
- The Secretary also held bilateral meetings between the senior most officials representing the states along with officials from the Ministry, to discuss challenges and strategies on a state-by-state basis.
Why Open Defecation + and Open Defecation ++?
- To ensure the sustainability and long term impact of the ODF status.
- The SBM ODF+ and SBM ODF++ protocols build upon the ODF protocol while keeping true to its provisions, so as to provide a platform for cities and towns to improve sanitation sustainability. The protocols are incremental in nature, and reflect on-ground realities present in India.
- What are the difference between Open Defecation + and Open Defecation ++?
- Cities and towns that have already achieved ODF status as per the ODF protocol prescribed by MoHUA and are working towards ensuring sustainability of the ODF status to ensure proper maintenance of toilet facilities are referred to as SBM ODF+.
- ODF ++ includes safe collection, conveyance, treatment and disposal of all faecal sludge and sewage besides the protocols of ODF+ in order to achieve safe sustainable sanitation for all. It is step further for enhanced sustainability of the sanitation in the cities.
- How will a city be included in ODF + and ODF++?
- After declared ODF, a city would need to follow the set criteria (protocol) so as to get certification of ODF+ and ODF++. The purpose would be to sustain its sanitation status of defecation free.
Definition of ODF+ city or ward?
- A city / ward / work circle1 can be notified/declared as SBM ODF+ city/ SBM ODF+ ward/SBM ODF+ work circle if, at any point of the day, not a single person is found defecating and/or urinating in the open
- Moreover, all community and public toilets are functional and well maintained.
- Cities that have been certified ODF at least once on the basis of the ODF Protocol laid down by ministry shall be eligible to declare themselves as SBM ODF+ and apply for certification of SBM ODF+ status. In other words cities which have been declared ODF by the government are eligible for ODF+.
What the definition of ODF++ city or ward?
- A city / ward / work circle can be notified/ declared as SBM ODF++ city/ SBM ODF++ ward/ SBM ODF++ work circle if, at any point of the day, not a single person is found defecating and/or urinating in the open, all community and public toilets are functional and well maintained.
- More over faecal sludge/septage and sewage is safely managed and treated, with no discharging and/or dumping of untreated faecal sludge/septage and sewage in drains, water bodies or open areas.
- Cities that have been certified SBM ODF+ at least once shall thereafter be eligible to declare themselves as SBM ODF++ and apply for certification of SBM ODF++ status.
- Pre requisites to achieve ODF+
- Individual toilets should be functional and well-maintained, with water availability.
- All public areas have functional public toilets within a span of 1 km.
- While deciding the number of toilet seats/urinals and blocks, the city’s entire floating population must have been considered.
- The city has sufficient mobile toilets/toilet facilities for use during occasions with large gatherings in a single area
- Once a city has communicated to the respective state government the final resolution declaring the city to be SBM ODF+, and the state government has communicated the same to MoHUA (or in case of development authority or cantonment board, city has directly communicated to MoHUA), a third party verification process (“Swachh Certification for SBM ODF+”) is to be adopted, for the final SBM ODF+ certification.
Prerequisites to achieve SBM ODF++
- All necessary conditions for SBM ODF+ (as per the SBM ODF+ protocol laid down by MoHUA) have been achieved, except that at least 25% of functional public and community toilets must adhere to the additional conditions.
- All toilets (individual, community and public) are either connected to (a) sewer networks; or (b.) safe containment systems (such as septic tanks, twin pits or other on-site sanitation systems prescribed by CPHEEO or under SBM-Urban Mission Guidelines).
7. Joint Exercise on Urban Earthquake Search and Rescue (SCOJtEx)-2019
- Context:India calls for cooperation among SCO nations to ensure peoples' safety from disasters
- All Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) nations must jointly make concerted, synchronized effort towards securing people from disasters, said Indian Home Minister Amit Shah here on Friday.
- Addressing the 10th meeting of the heads of departments of SCO member states, Shah said that climate change presented new challenges in disaster management in today's world.
- The meeting deals with the prevention and elimination of emergency situations. This was the first time when India hosted this meeting.
- He expressed confidence that the Joint Exercise on Urban Earthquake Search & Rescue (SCOJtEx)-2019 and the ministerial meeting would help in finalizing the action plan for managing disasters for the year 2020-2021.
(SCOJtEx-2019):Why in News?
- Union Minister of Home Affairs will inaugurate the Shanghai Cooperation Organization Joint Exercise on Urban Earthquake Search & Rescue (SCOJtEx-2019).
- SCO Urban Earthquake Search & Rescue Exercise (SCOJtEx.)-2019:
- The National Disaster Response Force (NDRF) is hosting the exercise.
- The main aim to rehearse the disaster response mechanism, share knowledge, experience, technology & also for mutual coordination, etc.
- This exercise shall also provide an opportunity to enhance the coordination & co-operation involving multi-agency operations in an earthquake scenario.
- The participants of all 08 member countries namely China, India, Kazakhastan, Kyrgyzstan, Pakistan, Russia, Tajikistan and Uzbekistan shall be participating in this exercise.
- The four day long simulation exercise shall be conducted as per the International Search & Rescue Advisory Group (INSARAG) methodology & guidelines.
- There will be a Joint Urban Earthquake Search & Rescue Exercise for Shanghai Cooperation Organization member states followed by the Shanghai Cooperation Organization experts meeting of Ministries responsible for Prevention and Elimination of Emergency Situation.
- The main focus of Shanghai Cooperation Organization Joint Exercise on Urban Earthquake Search & Rescue (SCOJtEx-2019) shall be to test the region’s preparedness and resilience towards effective activation of Inter- governmental interaction for immediate response.
INSARAG:
- The International Search and Rescue Advisory Group (INSARAG) was established in 1991.
- This establishment followed the initiatives of the specialised international Urban Search and Rescue (USAR) teams who operated together in the Mexican earthquake of 1985 and the Armenian earthquake of 1988.
- The INSARAG’s primary purpose is to facilitate coordination between the various international USAR teams who make themselves available for deployment to countries experiencing devastating events of structural collapse due primarily to earthquakes.
- The group achieves such coordination through facilitating opportunities for communication between these groups ahead of such events.
- These meetings of teams have resulted in many practical agreements between them that have streamlined working together during actual disasters
sponsors:







No comments:
Post a Comment