CURRENT AFFAIRS
16 OCTOBER 2019
BY SUMIT
IMPORTANT TOPICS IN THE CONTEXT OF INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS,
INDIAN HISTORY,INDIAN POLITY,ECONOMY AND SOCIETY,
ENVIRONMENT for TODAY TO LOOK AT .
1.International Monetary Fund (IMF)(gs-3)
Context: IMF cuts India’s growth projection to 6.1% in 2019
2.The Enforcement Directorate(ED)(gs-2,3)
Context: much in news….ED summons Praful in money laundering case
Chidambaram will also be interrgoted by ED
3.Air Quality Index (AQI),SAFAR (System of Air Quality and Weather Forecasting and Research).
(gs-3)
Context:Capital unable to breathe easy as air quality remains poor
4.Swachh Survekshan 2019
(gs-2,3)
Context: Govt. to probe ‘irregularities’ in M.P. Swachh survey
5.Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana(PMJAY)(gs-2)
Context:Gujarat, T.N. top performers under PM-JAY health scheme
6.Trade Deficit + Balance of Trade(gs-3)
Context: India’s exports decline 6.57% in September
7.World Food Day(gs-2,3)
Today is world food day and according to unicef-Every child on the planet has the right to nutritious,healthy food but a staggering 1 in 3 children today are either undernourished or overweight.
8.DRDO(gs-2,3)
Context:Will fight and win the next war with indigenous weapon systems: Army Chief to DRDO.
1.International Monetary Fund (IMF)(gs-3)
- Context: IMF cuts India’s growth projection to 6.1% in 2019
- The International Monetary Fund (IMF) in April said India will grow at 7.3% in 2019.
- The IMF on Tuesday slashed India’s GDP growth projection for the year 2019 to 6.1%, which is 1.2% down from its April projections.
- The International Monetary Fund (IMF) in April said India will grow at 7.3% in 2019. However, three months later it projected a slower growth rate for India in 2019, a downward revision of 0.3%.
- As against India’s real growth rate of 6.8% in 2018, the IMF in its latest World Economic Outlook projected India’s growth rate at 6.1% in 2019 and noted that the Indian economy is expected to pick up the next year at 7.0% in 2020.
The International Monetary Fund
- The International Monetary Fund or the IMF is a global organization with its headquarters at Washington, D.C. to promote international monetary cooperation, enable international trade, achieve financial stability, stimulate high employment, diminish poverty in the world and sustain economic growth.
- IMF was formed at the Bretton Woods Conference in 1944 and it was formally established a year later. Initially, there were 29 countries with a goal of redoing the global payment system. Today, the organization has 189 members.
- The IMF offers policy advice and financing to its members and works with developing countries to assist them in attaining macroeconomic stability and overcoming poverty. The logic for this is that private global capital markets operate imperfectly and many nations do not have enough access to financial markets.
2.The Enforcement Directorate(ED)(gs-2,3)
- Context: much in news….ED summons Praful in money laundering case
- Chidambaram will also be interrogated by ED
The Enforcement Directorate(ED):
- It is economic intelligence and law enforcement agency responsible for enforcing economic laws and fighting economic crime in India.
- It functions under aegis of Department of Revenue, Union Ministry of Finance.
- Its prime objective is enforcement of two key Acts of Government of India namely:
- Foreign Exchange Management Act 1999 (FEMA) and
- Prevention of Money Laundering Act 2002 (PMLA)
- to check money laundering by curb black money and hawala trade cases.
- It is composed of officers from the Indian Revenue Service, Indian Police Service and the Indian Administrative Service.
- It was established in 1956 as ‘Enforcement Unit’ in Department of Economic Affairs.
- It is headquartered in New Delhi.
3.Air Quality Index (AQI),SAFAR (System of Air Quality and Weather Forecasting and Research). (gs-3)
- Context:Capital unable to breathe easy as air quality remains poor
- The Air Quality Index (AQI) of Delhi worsened slightly on Tuesday and stayed in the “poor” category and is expected to further deteriorate from the last week of October. Meanwhile, stubble burning in Haryana, Punjab and on the border regions have shown a slight increase over the last 24 hours, according to governmentrun monitoring agency SAFAR (System of Air Quality and Weather Forecasting and Research). But SAFAR said that the share of external biomass burning (mainly stubble burning) from neighbouring States is only 5% of the total PM2.5 level in Delhi. PM2.5 is the main cause of pollution in Delhi at this point.
NATIONAL AIR QUALITY INDEX
- National Air Quality Index (AQI) has been launched for monitoring the quality of air in major urban centres across the country on a real-time basis and enhancing public awareness for taking mitigative action.
- The Union Environment Ministry proposes to extend the measurement of air quality to 22 state capitals and 44 other cities with a population exceeding one million.
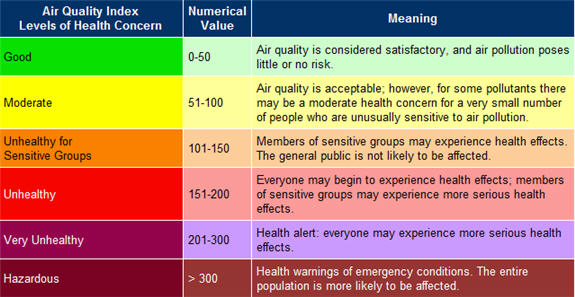
Salient features of the Index:
• The Index is centred around five chief pollutants: Particulate Matter, Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide and Carbon Monoxide.
• The unit of measurement is microgram (or milligram in the case of CO) per cubic meter.
• The AQI has been at present launched for 10 cities -- Delhi, Agra, Kanpur, Lucknow, Varanasi, Faridabad, Ahmedabad, Chennai, Bangalore and Hyderabad.
• The AQI has been developed by the Central Pollution Control Board in consultation with IIT-Kanpur and an expert group comprising medical, air-quality professionals and other stakeholders.
• India has joined the global league of countries like the US, China, Mexico and France that have implemented smog alert systems.
SAFAR:
- SAFAR stands for System of Air Quality and Weather Forecasting And Research
- It is a research program to build Air-Pollution mitigation strategies in consonance with nation’s economic development
- It is launched in greater metropolitan cities of India to provide location specific information on air quality in near real time
- It has been combined with the early warning system on weather parameters
- The ultimate objective of the project is to increase awareness among general public regarding the air quality in their city well in advance so that appropriate mitigation measures and systematic action can be taken up for betterment of air quality and related health issues.
- SAFAR was developed indigenously by Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM), Pune and operationalized by India Meteorological Department (IMD).
- Pollutants monitored: PM1, PM2.5, PM10, Ozone, CO, NOx (NO, NO2), SO2, BC, Methane (CH4), Non-methane hydrocarbons (NMHC), VOC’s, Benzene, Mercury.
- Monitored Meteorological Parameters: UV Radiation, Rainfall, Temperature, Humidity, Wind speed, Wind direction
4.Swachh Survekshan 2019(gs-2,3)
- Context: Govt. to probe ‘irregularities’ in M.P. Swachh survey
- The Union Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs has initiated an inquiry into alleged irregularities during the Swachh Survekshan 2019 for Madhya Pradesh — declared the best in solid waste management, and boasting eight cities in the top 25, the most for any State — that helped upstage certain cities, while downplaying performances of others.
Swachh Survekshan 2019:
Success of Swachh Bharat
- The recently concluded Swachh Survekshan 2018 ranked 4,203 Cities.
- Swachh Survekshan has caught the imagination of citizens and stakeholder alike: in 2016, 1 lakh citizens provided their feedback in the survey.
- In 2017, nearly 20 lakh citizen feedback was received. 2018 garnered feedback from 38 lakh citizens, a milestone to the way in which the SBM has become an integral part of citizens’ mental maps.
- The survey has already succeeded in fostering a spirit of healthy competition among towns and cities to improve their service delivery to citizens, towards creating cleaner cities.
Highlights of Swachh Survekshan 2018
- 79% of residents find their area cleaner than last year
- 73,875 waste pickers provided formal livelihood
- In 137 cities, > 60% of the bulk garbage generators are doing on-site composting
- 33% cities of >1 lakh population have ICT based monitoring of their Community and Public Toilets
Swachh Survekshan 2019
- With an aim to increase the coverage of the ranking exercise MoHUA now proposes to conduct its fourth survey – Swachh Survekshan 2019 to rank all cities under Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban (SBM-U).
- The distinctive features of the survey includes encouraging large scale citizen participation, ensuring sustainability of initiatives taken towards garbage free and open defecation free cities, providing credible outcomes which would be validated by third party certification etc.
- The Swachh Survekshan 2019 toolkit that will be launched will contain the detailed survey methodology and component indicators with scores to help cities to prepare themselves for taking the survey.
- SBM ODF+ and ODF++ Protocol
- The SBM ODF+ protocol focuses on sustaining community/ public toilet usage by ensuring their functionality, cleanliness and maintenance.
- The SBM ODF++ will focus on achieving sanitation sustainability by addressing complete sanitation value chain, including safe containment, processing and disposal of fecal sludge and septage.
- The ODF+ and ++ protocol and toolkit to be launched will detail out the necessary conditions to be achieved by cities for declaring themselves as ODF+ and ODF++, along with the detailed steps required for third party certifications.
Swachh Manch web portal
- It is a web-based platform which aims to bring together every stakeholder contributing to the Swachh Bharat Mission under a common platform.
- It will allow stakeholders to create/invite/participate in volunteering opportunities around neighborhoods.
- It will enable uploads of pictorial evidence of citizens and organizations participating in the initiatives, as well as record the number of hours volunteered, as acknowledgement of citizens’/organisations’ efforts and contributions to the cause of ‘swachhata’.
- The Swachh Manch will also be integrated with the existing Swachhata App to act as a citizens’ grievance redressal platform.
Ease of Living Index
- The Ease of Living assessment standards are closely linked to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and will provide a strong impetus to India’s effort for systematic tracking progress of SDGs in the urban areas.
- It will also be launched along with an Ease of Living Index dashboard.
- Apart from presenting the overall national ranking of 111 cities, the dashboard will present ranking of the cities across pillars, category, geographical zone and population classifications.
- This framework comprises four pillars namely Institutional, Social, Economic and Physical which are further broken down into 15 categories and 78 indicators.
- The dashboard will also have a comparison feature that will allow users to analyse the performance across cities on various liveability parameters.
5.Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana(PMJAY)(gs-2)
Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana(PMJAY):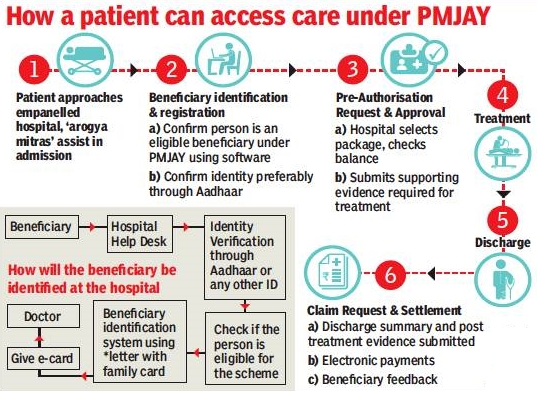
Trade Deficit + Balance of Trade
Today is world food day and according to unicef-Every child on the planet has the right to nutritious, healthy food but a staggering 1 in 3 children today are either undernourished or overweight.
- Context:Gujarat, T.N. top performers under PM-JAY health scheme
- Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, Chhattisgarh, Kerala and Andhra Pradesh have emerged as the top performing States with free secondary and tertiary treatment worth nearly rs 7,901 crore availed under the Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PMJAY), the flagship health assurance scheme of the Government in just over a year. “Halfacrore hospital treatments have been provided and there are 9 hospital admissions every minute across India,’’ noted a senior health offi??cial. Launched last year, the scheme crossed the 50lakh treatment mark this week with secondary and tertiary level treatments worth rs 7,901 crore being carried out across 32 States and Union Territories.
Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana(PMJAY):

- Ministry : Ministry of Health and Family Welfare
- Aims to reduce the financial burden on poor and vulnerable groups arising out of catastrophic hospital episodes and ensure their access to quality health services.
- Scheme:
- PM-JAY is a scheme of the government under Ayushman Bharat.
- PMJAY is government-sponsored health insurance scheme, that will provide free coverage of up to Rs 5 lakh per family per year in any government or empanelled private hospitals all over India.
- It will cover beneficiaries families identified on the basis of Socio Economic Caste Survey (SECC) 2011 in 444 districts of 30 states/Union Territories.
- National Health Agency (NHA) is the apex body for implementing this scheme.
- States will be required to form State Health Agency (SHA) to implement scheme and at the district level also structure for its implementation will be set up.
- Around 13000 hospitals both public and private in the country have been coordinated for implementation of the scheme.
- PMJAY will be funded with 60% contribution from Centre and remaining from the states.
- NITI Aayog will be working as partner for this scheme for operationalizing robust, modular and interoperable IT platform which will involve a paperless and cashless transaction.
- PMJAY is entitlement based scheme with entitlement decided on basis of deprivation criteria in the SECC database.
- There will be no cap on family size and age under this scheme.
- The benefit cover under it also includes pre and post-hospitalisation expenses.
- It also takes into consideration all pre-existing medical conditions.
- It will provide reimbursement for bed charges and drugs and diagnostics two days before, during and 15 days after hospitalisation. Beneficiary will be also paid transport allowance for hospitalisation defined under it.
- The payment for treatment will be done on package rate which will be defined by Government in advance basis.
- The package rates will include all costs associated with treatment.
- States and UTs have flexibility to modify these rates within limited bandwidth.
- PMJAY allows national portability i.e. resident of any part of country is entitled for free hospitalization at empanelled hospital anywhere in the country.
- It will strengthen healthcare services in India by targeting poor and vulnerable population of the country.
- The scheme allows beneficiary to take cashless benefits from any public or private empanelled hospitals across the country.
- ID documentation required for verifying beneficiary under this scheme may be Aadhaar card or election ID card or ration card.
- Aadhaar is not mandatory.
- Beneficiaries will QR codes having letters for verification through scanning.
- Scheme also seeks to accelerate India’s progress towards the achievement of Universal Health Coverage (UHC) and Sustainable Development Goal – 3 (SDG3).
6.Trade Deficit + Balance of Trade(gs-3)
- Context: India’s exports decline 6.57% in September
- India’s exports remained in the negative zone for the second consecutive month in September contracting by 6.57% to $26 billion mainly due to significant dip in shipments of petroleum, engineering, gems and jewellery and leather products
Trade Deficit + Balance of Trade
- A trade deficit occurs when a country’s imports exceeds its exports.
- In this situation, there is an outflow of domestic currency to foreign markets. Here, the balance of trade is said to be negative or unfavourable.
- Informally, there is said to be a trade gap. In contrast, if a country exports more than it imports, the trade balance is said to be positive or favourable.
- Then there is said to be a trade surplus.
- The balance of trade of a nation is a part of the current account.
- The current account also comprises of other transactions like the income from the NIIP or the net international investment position and international aid.
- When a country’s current account is in surplus, its net international asset position rises accordingly. Needless to say, a trade deficit brings down a country’s net international asset position.
- The balance of trade is also called the net exports or the commercial balance.
- India has a trade deficit and the average balance of trade was US$ -2314.14 million from 1957 to 2017.
7.World Food Day(gs-2,3)
Today is world food day and according to unicef-Every child on the planet has the right to nutritious, healthy food but a staggering 1 in 3 children today are either undernourished or overweight.
- World Food Day is celebrated by several organisations which are concerned with food security like International Fund for Agricultural Development, the World Food Program, etc. This day generates awareness globally for those who suffer from hunger and to ensure the need for food security and nutritious diets for all. The main focus of this day is that food is a basic and fundamental human right.
World Food Day 2019: Theme
- The theme of World Food Day 2019 is “Our Actions Are Our Future. Healthy Diets for A #ZeroHunger World". It focuses on tackling global hunger. Due to globalisation, urbanisation and income growth, our diets and eating habits are changed. Instead of seasonal, fibre rich food and plant based food we are shifted to refined, starches, sugar, fats, salt, processed food, meat, etc. It has been seen that in urban areas time spent on preparing food or meals is very less because people these days rely on ready mate food, supermarkets, fast food, street food, etc.
- Due to unhealthy diets and sedentary lifestyles obesity in people is increasing in developed, low-income countries. According to FAO, 670 million adults and 120 million girls and boys of the age group 5 to 18 years are obese and 40 million children under 5 are overweight. Around 820 million people suffer from hunger.
8.DRDO(gs-2,3)
- Context:Will fight and win the next war with indigenous weapon systems: Army Chief to DRDO.
- Chief of Army Staff General Bipin Rawat on Monday said that the armed forces will fight and win the next war with the indigenous weapon systems and pitched for greater inclusion of home-grown technology in the forces. The General was addressing the 41st DRDO Directors Conference in New Delhi.
DRDO:
- DRDO works under the administrative control of Ministry of Defence, Government of India.
- It is working to establish world class science and technology base for India and provides our Defence Services decisive edge by equipping them with internationally competitive systems and solutions.
- Dr G. Satheesh Reddy is the incumbent Chairman of DRDO.
Genesis & Growth
- DRDO was established in 1958 after combining Technical Development Establishment (TDEs) of the Indian Army and the Directorate of Technical Development & Production (DTDP) with the Defence Science Organisation (DSO).
- Starting with 10 laboratories, DRDO has now grown to a network of 52 laboratories which are deeply engaged in developing defence technologies covering various disciplines, like aeronautics, armaments, electronics, combat vehicles, engineering systems, instrumentation, missiles, advanced computing and simulation, special materials, naval systems, life sciences, training, information systems and agriculture.
- Presently, the Organisation is backed by over 5000 scientists and about 25,000 other scientific, technical and supporting personnel.
- Several major projects for the development of missiles, armaments, light combat aircrafts, radars, electronic warfare systems etc are on hand and significant achievements have already been made in several such technologies.
Mission
- Design, develop and lead to production state-of-the-art sensors, weapon systems, platforms and allied equipment for our Defence Services.
- Provide technological solutions to the Services to optimise combat effectiveness and to promote well-being of the troops.
- Develop infrastructure and committed quality manpower and build strong indigenous technology base.
- Integrated Guided Missile Development Programme (IGMDP)
- IGMDP was brain child of renowned scientist Dr. APJ Abdul Kalam.
- It was intended to attain self-sufficiency in the field of missile technology.
- After keeping in mind the requirements of various types of missiles by the defense forces, the program recognized the need to develop five missile systems.
- The IGMDP formally got the approval of Indian government on July 26, 1983.
- It brought together the country’s scientific community, academic institutions, R&D laboratories, industries and the three defence services in giving shape to the strategic, indigenous missile systems.
The missiles developed under IGMDP are:
- Short-range surface-to-surface ballistic missile – Prithvi
- Intermediate-range surface-to-surface ballistic missile – Agni
- Short-range low-level surface-to-air missile – Trishul
- Medium-range surface-to-air missile – Akash
- Third generation anti-tank missile – Nag
- The Agni, which was initially conceived as a technology demonstrator project in the form of a re-entry vehicle, was later upgraded to a ballistic missile with different ranges. Dr. Kalam played a major role in the development and operationalisation of Agni and Prithvi missiles.
- After achieving the goal of making India self-reliant in missile technology, DRDO on January 8, 2008, formally announced successful completion of IGMDP.






No comments:
Post a Comment