DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS 16 SEPTEMBER 2019
BY SUMIT BHARDWAJ
IMPORTANT NEWS ARTICLES
ANALYSIS
1.Saudis to tap oil reserves after drone attacks on Aramco plants(GS-2,3)
- CONTEXT:Saudi Arabia will use its vast oil reserves to offset disruption to production, Energy Minister Prince Abdulaziz bin Salman said on Sunday. Drone attacks on two major oil facilities on Saturday knocked 5.7 million barrels per day (bpd) off production — close to 6% of the global crude supplies.
- Between 1988 and 2009, Riyadh had built five giant underground storage facilities across the country to be used during crises.
- The drone strikes on Saturday on national energy giant Aramco’s processing plants in Abqaiq and Khurais knocked 5.7 million barrels per day (bpd) off production, close to 6% of the global crude oil supplies.
- Riyadh has built five giant underground storage facilities across the country that can hold tens of millions of barrels of various refined petroleum products, to be tapped into during times of crisis. The facilities were constructed between 1988 and 2009 and cost tens of billions of dollars.
- The disruption represents half the output of the kingdom, which is the world’s biggest oil supplier.
- Prince Abdulaziz said Saturday’s explosions also halted supplies of some two billion cubic feet of associated gas, extracted along with the crude.
- Last month, an attack also claimed by Huthi rebels sparked a fire at Aramco’s Shaybah natural gas liquefaction facility, close to the Emirati border, with no casualties reported.
- The Houthis also claimed a May drone attack on two oil pumping stations on Saudi Arabia’s key east-west pipeline, which caused a days-long shutdown.
The Houthi insurgency :
- The Houthi insurgency in Yemen,also known as the Houthi rebellion, Sa'dah War, or Sa'dah conflict, was a military rebellion pitting Zaidi Shia Houthis (though the movement also includes Sunnis) against the Yemeni military that began in Northern Yemen and has since escalated into a full-scale civil war. The conflict was sparked in 2004 by the government's attempt to arrest Hussein Badreddin al-Houthi, a Zaidi religious leader of the Houthis and a former parliamentarian on whose head the government had placed a $55,000 bounty.Initially, most of the fighting took place in Sa'dah Governorate in northwestern Yemen, but some of the fighting spread to neighbouring governorates Hajjah, 'Amran, al-Jawf and the Saudi province of Jizan. Since 2014 the nature of the insurgency has changed with the Houthi takeover in Yemen and then into the ongoing Yemeni civil war (2015–present) with a major Saudi-led intervention in Yemen beginning in 2015.
- General Ali Mohsen al-Ahmar commanded the Yemeni security forces during the conflict and led all the government offensives from 2004 until 2011, when he resigned his post to defend protesters during the Yemeni Revolution.
- A Houthi power grab in Sanaa escalated on 20 January 2015, when the rebels attacked the president's residence and swept into the presidential palace. President Abed Rabbo Mansour Hadi was inside the residence as it came under "heavy shelling" for half an hour, but he was unharmed and protected by guards, according to Information Minister Nadia Al-Sakkaf. Presidential guards surrendered the residence after being assured that Hadi could safely evacuate. The U.N. Security Council called an emergency meeting about the unfolding events. United Nations Secretary-General Ban Ki Moon expressed concern over the "deteriorating situation" in Yemen and urged all sides to cease hostilities.[On 22 January, President Abed Rabbo Mansour Hadi and Prime Minister Khaled Bahah tendered their resignations to parliament, which reportedly refused to accept them.
- Aramco:Saudi Aramco, officially the Saudi Arabian Oil Company, is a Saudi Arabian national petroleum and natural gas company based in Dhahran, Saudi Arabia. It is one of the largest companies in the world by revenue, and according to accounts seen by Bloomberg News, the most profitable company in the world
ARMACO- INDIA RELATIONS:
- RECENT DEVELOPMENTS BETWEEN THE BOTH:
- An Indian consortium comprising IOCL, BPCL and HPCL has signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with Saudi Aramco, the world’s largest oil producer to jointly develop and build Ratnagiri Refinery in Maharashtra.
- Reliance Industries Ltd (RIL) is in the process of selling a 20% stake in the company’s flagship chemicals and refining business to Saudi Aramco in a deal valued at $15 billion, as the Indian company seeks to cut its massive debt and secure an assured supply of crude oil to its refineries.
OPEC (ORGANIZATION OF THE PETROLEUM EXPORTING COUNTRIES ):
- The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) is a group of oil-producing nations that was first established in Baghdad, Iraq, in 1961. OPEC is one of the most powerful international organizations in the world and was a major player in the shift towards state control over natural resources.
Membership:
- The OPEC Statute distinguishes between the Founder Members and Full Members – those countries whose applications for membership have been accepted by the Conference.
- The Statute stipulates that “any country with a substantial net export of crude petroleum, which has fundamentally similar interests to those of Member Countries, may become a Full Member of the Organization, if accepted by a majority of three-fourths of Full Members, including the concurring votes of all Founder Members.”
- The Statute further provides for Associate Members which are those countries that do not qualify for full membership, but are nevertheless admitted under such special conditions as may be prescribed by the Conference.
- Currently, the Organization has a total of 15 Member Countries. The current OPEC members are the following: Algeria, Angola, Ecuador, Equatorial Guinea,
- Gabon, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Libya, Nigeria, Qatar, the Republic of the Congo, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, and Venezuela.
- Indonesiais a former member, and Qatar will no longer be the member of OPEC starting on 1 January 2019.
2.Vulture culture: How the bird was saved from extinction(GS-3)
- CONTEXT:In the late 1990s, when the population of the vultures in the country had begun to decline sharply, one White-backed vulture was rescued from Keoladeo National Park in Rajasthan, where vultures were dying at an alarming rate.
- To study the cause of deaths of vultures, a Vulture Care Centre (VCC) was set up at Pinjore, Haryana. It was here that the rescued vulture from Rajasthan was brought. Later, a few more vultures from Haryana, Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh were brought in.
- Starting with just a few vultures, the VCC, until then the sole facility for conservation of vultures in the country, has come a long way in the past two decades. At present there are nine Vulture Conservation and Breeding Centres (VCBC) in India, of which three are directly administered by Bombay Natural History Society (BNHS).
Keoladeo National Park in Rajasthan:
- Keoladeo National Park or Keoladeo Ghana National Park formerly known as the Bharatpur Bird Sanctuary in Bharatpur, Rajasthan, India is a famous avifauna sanctuary that hosts thousands of birds, especially during the winter season. Over 230 species of birds are known to be resident. It is also a major tourist centre with scores of ornithologists arriving here in the hibernal season. It was declared a protected sanctuary in 1971. It is also a World Heritage Site.
- Keoladeo Ghana National Park is a man-made and man-managed wetland and one of the national parks of India. The reserve protects Bharatpur from frequent floods, provides grazing grounds for village cattle, and earlier was primarily used as a waterfowl hunting ground. The 29 km2 (11 sq mi) reserve is locally known as Ghana, and is a mosaic of dry grasslands, woodlands, woodland swamps and wetlands. These diverse habitats are home to 366 bird species, 379 floral species, 50 species of fish, 13 species of snakes, 5 species of lizards, 7 amphibian species, 7 turtle species and a variety of other invertebrates.Every year thousands of migratory waterfowl visit the park for wintering and breeding. The sanctuary is one of the richest bird areas in the world and is known for nesting of resident birds and visiting migratory birds including water birds. The rare Siberian cranes used to winter in this park but this central population is now extinct. According to founder of the World Wildlife Fund Peter Scott, Keoladeo National Park is one of the world’s best bird areas
Jatayu Conservation Breeding Centre, Pinjore:
 |
- The Vulture Conservation Breeding Centre (VCBC) is a joint project of the Haryana Forest Department and the Bombay Natural History Society (BNHS). It is a collaborative initiative to save the three species of vultures, the White-backed, Long-billed and Slender-billed, from looming extinction.
- The VCBC, earlier known as Vulture Care Centre (VCC), was established in September 2001 with the UK Government's 'Darwin Initiative for the Survival of Species' fund, to investigate the dramatic declines in India's Gyps species of vultures.
- Subsequent to the release of the South Asia Vulture Recovery Plan in February 2004, the VCC was adapted and upgraded to being the first VCBC, in line with a key recommendation of the Recovery Plan to set up a conservation breeding programme for the three critically endangered species of vultures. The centre sprawls over 5 acres of Haryana Forest Department's land at village Jodhpur. The Jatayu Conservation Breeding Centre (JCBC) is a joint project of the Haryana Forest Department and the Bombay Natural History Society (BNHS).It is a collaborative initiative to save the three species of vultures, the White-backed, Long-billed and Slender-billed, from looming extinction. The centre is located at village Jodhpur on the edge of the Bir Shikargaha Wildlife Sanctuary which is about 8 km off the National Highway-22 from Pinjore on Mallah Road. The centre is spread on a 5 acre land of Haryana Forest Department.
- The JCBC, earlier known as Vulture Care Centre (VCC), was established in September 2001 with the UK Government Darwin Initiative for the Survival of Species’ fund, to investigate the dramatic declines in the resident Gyps species of vultures.
- Subsequent to the release of the South Asia Vulture Recovery Plan in February 2004, the VCC was adapted and upgraded to being the first JCBC, in line with a key recommendation of the Recovery Plan to set up a conservation breeding programme for the three critically endangered Gyps species of vultures.
- At present the centre houses a total 160 Vultures which includes 63 White-backed Vultures, 74 Long-billed Vultures, 21 Slender-billed Vultures and 2 Himalayan Griffons. This is the largest collection of the three critically endangered Gyps species of vulture at one place anywhere in the world.
The Bombay Natural History Society, founded on 15 September 1883, is one of the largest non-governmental organisations in India engaged in conservation and biodiversity research. It supports many research efforts through grants and publishes the Journal of the Bombay Natural History Society. Many prominent naturalists, including the ornithologists Sálim Ali and S. Dillon Ripley, have been associated with it.The society is commonly known by its initials, BNHS. BNHS is the partner of BirdLife International in India. It has been designated as a 'Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation' by the Department of Science and Technology. Its headquarter is in Mumbai and has one regional centre at Wetland Research and Training Centre, near Chilika Lake, Odisha
3.Survey of India to deploy 300 drones for mapping country.(GS-2,3)
- CONTEXT:India’s oldest scientific department, the Survey of India (SoI) — historically tasked with mapping the country — will for the first time rely on drones to map the country.
- Other than unprecedented detail, a consequence of the mapping will be creating high resolution maps of land in villages facilitating the digitisation of land titles in villages, according to officials involved with the survey.
- Currently the best SoI maps have a resolution of 1:250000, meaning a 1 cm on the map represents 2500 cm on the ground. The maps being prepared, according to senior officials associated with the project will be of 1:500 resolution, meaning 1 cm will represent 500 cm.
- The aim is to map 75% of India’s geography— about 2.4 million sq km of the 3.2 million sq km — within the next two years. The organisation aims to procure about 300 drones — so far about 30 have been sourced — for the gargantuan exercise. However forests, hills and deserts are likely to be left out.
- As a prelude, the SoI, which is affliated to the Department of Science and Technology (DST), has signed agreements with 6 districts in Haryana, 2 in Karnataka and 2 in Maharashtra to undertake such drone-based mapping exercises. Every square kilometre mapped by drones will be encapsulated in 2500 pictures and thus be a trove of digital data.
Sorting rural issues
- A major consequence of the drone-based exercise will be the mapping of settled habitations in villages (called abaadi areas in legal parlance). Based on the availability of accurate maps, residents will finally be able to get property cards as well as proper legal titles to their lands. “This is unprecedented in the history of independent India and we’ve already executed a project in Maharashtra,” said Mr. Kumar.
Survey of India (SoI) :
The Survey of India is India's central engineering agency in charge of mapping and surveying.Set up in 1767 to help consolidate the territories of the British East India Company, it is one of the oldest Engineering Departments of the Government of India. Its members are from Survey of India Service cadre of Civil Services of India and Army Officers from the Indian Army Corps of Engineers. It is headed by the Surveyor General of India. At present, Survey of India is headed by Lt Gen Girish Kumar, VSM.
SI (cartography) as well as ASI (archaeology), BSI (botany), FSI (forests), FiSI (fisheries), GSI (geology), IIEE (ecology), NIO (oceanography), RGCCI (Census of India) and ZSI (zoology) are key national survey organisations of India.
HISTORY
The-history of the Survey of India dates back to the 18th Century . "First modern scientific survey of India" was undertaken by W. Mather in 1793–96 on instructions of Superintendent of Salem and Baramahal, Col. Alexander Read. The present Dharmapuri district, Krishnagiri district and North Arcot in western Tamil Nadu were then called Baramahal.
Great Trigonometrical Survey (1802–1852) was started by British surveyor Col. William Lambton on 10 April 1802 from St. Thomas Mount in Chennai to foothills of Himalayas. 36 inch huge half ton weight Theodolite was used, which took 57 days to measure the 12-km base line. This 5-decade project was completed under Survey General Lt. George Everest in the year 1852. Pioneering mathematician and Surveyor Radhanath Sikdar measured Mount Everest in 1852, with a height of 29,002 feet. Modern measurements indicate the height is 29,037 feet. This is regarded as the beginning of a new age of systematic topographical mapping in India succeeding the classical age, and the founding of one of the oldest survey and mapping agencies in the world".
Organisation
The Survey of India, headquartered at Dehra Dun, has 18 Geo Spatial divisions ranging from the prediction of tides to aerial survey. It has 23 Geo-spatial Data Centers spread across India, each catering to the respective administrative area. Surveyors are the back bone of Survey of India. Appointments to Group 'A' Civil Stream posts in the Junior Time Scale (Dy Supdtg Surveyor) in Survey of India are made on the basis of competitive Indian Engineering Services examination conducted by the Union Public Service Commission and also through permanent secondment of Army Officers Defence Stream by the Union Public Service Commission. The important posts/ grades in Survey of India are in the following order of seniority: Draftsman, Plane Tabler, Survey Assistant, Surveyor, Officer Surveyor, Deputy Superintending Surveyor, Superintending Surveyor, Superintending Surveyor (Non-Functional Second Grade)/Deputy Director, Director/Deputy Surveyor General, Additional Surveyor General, Surveyor General..
Responsibilities
Advisor to Govt: Survey of India acts as adviser to the Government of India on all cartography of India related matters, such as geodesy, photogrammetry, mapping and map reproduction.
Geo names: Survey of India is responsible for the naming convention and spellings of names of geographical features of India.
Certification and publication: Scrutiny and certification of external boundaries of India and Coastline on maps published by the other agencies including private publishers. Publication of tide tables (one year in advance) and maps of India.
Surveys: geodetic datum, geodetic control network, topographical control, geophysical surveys, cadastral surveying, geologic maps, aeronautical charts within India, such as for forests, army cantonments, large scale cities, guide maps, developmental or conservation projects, etc.
National borders: Demarcation of the borders and external boundaries of India as well as advice on the demarcation of inter-state boundaries.
Oceanic tidal prediction: Undertake prediction of tides at 44 ports including 14 foreign ports.
Research and development: In the area of photogrammetry, cartography, geodesy, topographical surveys and indigenisation of technology.
Training: Training for the central and state government departments as well as from foreign countries.
4.GODAVARI RIVER(GS-1)
CONTEXT: Eight dead, 37 missing as boat capsizes in fLooded GodavariThe Godavari is the largest river system of the Peninsular India and is revered as Dakshina Ganga.
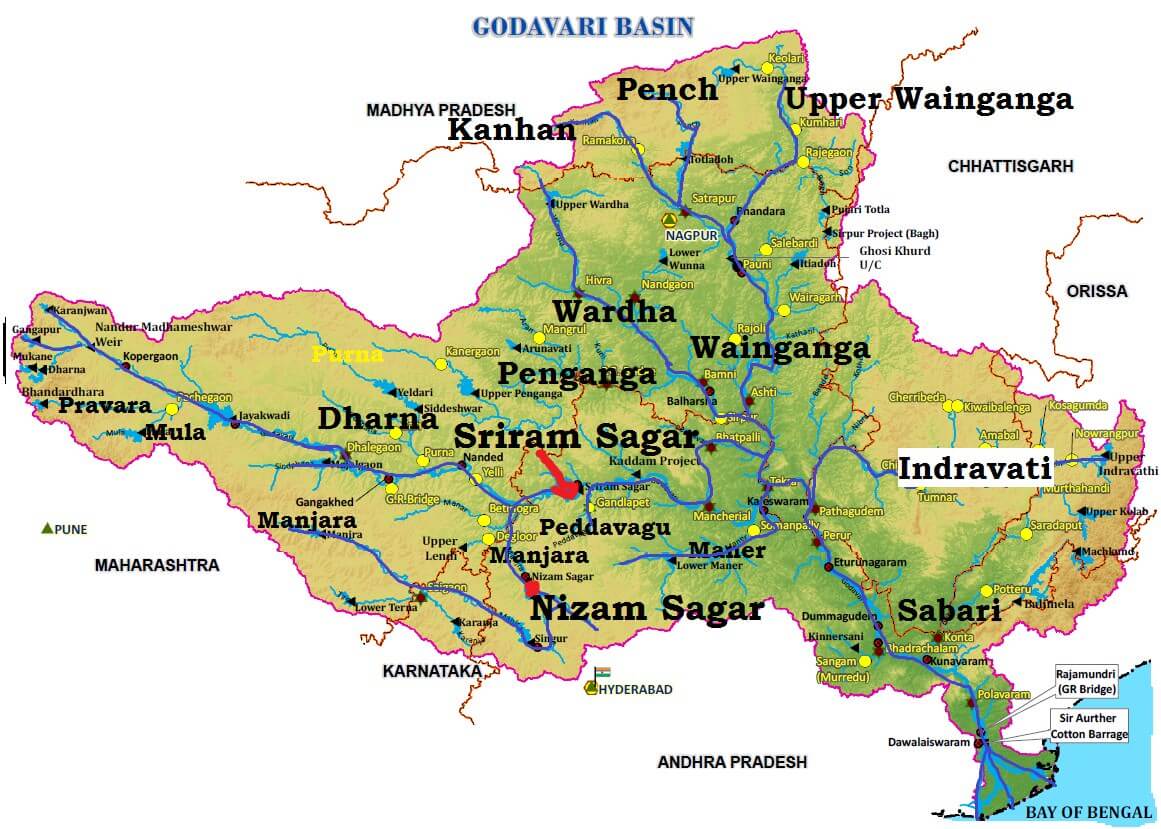
The Godavari basin extends over states of Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Chhattisgarh and Odisha in addition to smaller parts in Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka and Union territory of Puducherry (Yanam) having a total area of ~ 3 lakh Sq.km.
The basin is bounded by Satmala hills, the Ajanta range and the Mahadeo hills on the north, by the Eastern Ghats on the south and the east and by the Western Ghats on the west.
The Godavari River rises from Trimbakeshwar in the Nashik district of Maharashtra about 80 km from the Arabian Sea at an elevation of 1,067 m.
The total length of Godavari from its origin to outfall into the Bay of Bengal is 1,465 km.
The left bank tributaries are more in number and larger in size than the right bank tributaries.
The Manjra (724 km) is the only important right bank tributary. It joins the Godavari after passing through the Nizam Sagar.
Left Bank Tributaries: Dharna, Penganga, Wainganga, Wardha, Pranahita [conveying the combined waters of Penganga, the Wardha and Wainganga], Pench, Kanhan, Sabari, Indravati etc.
Right Bank Tributaries: Pravara, Mula, Manjra, Peddavagu, Maner etc.
Below Rajahmundry, the river divides itself into two main streams, the Gautami Godavari on the east and the Vashishta Godavari on the west and forms a large delta before it pours into the Bay of Bengal.
The delta of the Godavari is of lobate type with a round bulge and many distributaries.
Mineral Resources in Godavari Basin
The upper reaches of the Godavari drainage basin are occupied by the Deccan Traps containing minerals like magnetite, epidote, biotite, zircon, chlorite etc (metallic minerals)..
The middle part of the basin is principally composed of phyllites, quartzites, amphiboles and granites (rocks).
The downstream part of the middle basin is occupied mainly by sediments and rocks of the Gondwana group.
The Gondwanas are principally detritals (waste or debris, in particular organic matter produced by decomposition or loose matter produced by erosion) with some thick coal seams. [Singareni Coal Seam]
The Eastern Ghats dominate the lower part of the drainage basin and are formed mainly from the Khondalites..
Projects on Godavari River
Important projects completed duing the plan period are Srirama Sagar, Godavari barrage, Upper Penganga, Jaikwadi, Upper Wainganga, Upper Indravati, Upper Wardha.
Among the on-going projects, the prominent ones are Prnahita-Chevala and Polavaram.
Industry in Godavari Basin
The major urban Centers in the basin are Nagpur, Aurangabad, Nashik, Rajhmundry.
Nashik and Aurangabad have large number of industries especially automobile.
Other than this, the industries in the basin are mostly based on agricultural produce such as rice milling, cotton spinning and weaving, sugar and oil extraction.
Cement and some small engineering industries also exist in the basin.
Floods and Droughts in Godavari Basin
Godavari basin faces flooding problem in its lower reaches.
The coastal areas are cyclone-prone.
The delta areas face drainage congestion due to flat topography.
A large portion of Maharashtra falling (Marathwada) in the basin is drought prone.
5.Gooseberry candy(GS-1,3)
CONTEXT:Women who were given ironfolic acid tablets and reported unpleasant effectscould opt for alternative.
A drive for good nutrition among pregnant women and children in a southern Assam district has been given a gooseberry candy twist. This follows a report that the targeted groups find the prescribed ironfolic acid tablets repulsive. According to the 2015 National Family Health Survey, 47.2% of the women of reproductive age in Hailakandi were anaemic. The district, thus, has the most anaemic children below 5 years, adolescents and women of reproductive age in Assam. But mothers, pregnant women and children in the district, data reveal, consume only 24.3% of the total ironfolic acid tablets that the district receives and distributes
Amla, jaggery combo
To get around the problem while launching Poshan Maah, or nutrition month, a few days ago, the district administration decided to produce roundish amla-gur candies with a dose of salt. Nutritionists involved in the campaign said amla, or gooseberry, is rich in Vitamin C and antioxidants, while gur, or jaggery, is rich in iron, vital vitamins and minerals that boost the immune system.
The gooseberry with scientific names Ribes uva-crispa (and syn. Ribes grossularia), is a species of Ribes (which also includes the currants).
It is native to Europe, the Caucasus and northern Africa. The species is also sparingly naturalized in scattered locations in North America. Gooseberry bushes produce an edible fruit and are grown on both a commercial and domestic basis. Its native distribution is unclear, since it may have escaped from cultivation and become naturalized. For example, in Britain, some sources consider it to be a native,others to be an introduction.
Although usually placed as a subgenus within Ribes, a few taxonomists treat Grossularia as a separate genus, although hybrids between gooseberry and blackcurrant (e.g., the jostaberry) are possible. The subgenus Grossularia differs somewhat from currants, chiefly in their spiny stems, and in that their flowers grow one to three together on short stems, not in racemes. It is one of several similar species in the subgenus Grossularia; for the other related species (e.g., North American gooseberry Ribes hirtellum), see the genus page Ribes.
About Poshan Maah (National Nutrition Month):
The primary objective of the celebration of Poshan Maah is to take the messages of POSHAN to the grass root level.
The programme- an initiative of WCD Ministry and NITI Aayog is supported by 18 line Ministries/Departments/Government Organizations.
It seeks to synergise all efforts by leveraging technology and intends to take nutrition awareness to the level of Jan Andolan or People’s Movement.
The programme focuses on 8 themes – Antenatal Care, Optimal Breastfeeding (Early & Exclusive), Complementary Feeding, Anemia, Growth Monitoring, Girls-education, diet, right age of Marriage, Hygiene & Sanitation, Food Fortification.
About POSHAN Abhiyan:
POSHAN Abhiyaan (National Nutrition Mission) was launched on 8th March, 2018.
Objectives: The programme through use of technology, a targeted approach and convergence strives to reduce the level of Stunting, Under-nutrition, Anemia and Low Birth Weight in Children, as also, focus on Adolescent Girls, Pregnant Women & Lactating Mothers, thus holistically addressing malnutrition.
Aims: POSHAN Abhiyaan aims to ensure service delivery and interventions by use of technology, behavioural change through convergence and lays-down specific targets to be achieved across different monitoring parameters over the next few years.
Coverage: To ensure a holistic approach, all 36 States/UTs and 718 districts will be covered in a phased manner by the year 2020.
6.‘10 Hafte 10 Baje 10 Minute‘:Anti-dengue campaign(GS-2)
- CONTEXT:Fight against dengue: DELHI CM visits residential areas
- DELHI CM on Sunday visited residential areas to encourage Delhiites to join the campaign he started to clean stagnant water once a week as part of the fight against dengue. He visited residents in the Gole Market area of his constituency, Kohat Enclave and Burari. Speaking at Gole Market, the CM said: “In 2015, 15,000 people contracted dengue and 60 people lost their lives. In 2018, Delhi had just 2,700 cases. We were warned by doctors that this year there is likely to be a sudden spike in cases because the dengue outbreak follows a cycle of 34 years. We don’t want Delhi to suffer from an epidemic. That is why we have started this mega drive against dengue.”
WHAT THIS YOJANA FOCUSES ON:
- The best preventive measure for residents living in areas infested with Aedes aegypti is to clean the places where the mosquito lays their eggs, primarily artificial containers that store water.
- Items that collect rainwater or are used to store water (for example, plastic containers, drums, buckets, or used automobile tires) should be cleaned or discarded.
- Pet watering containers and flower vases should be emptied and scrub dried at least once a week. This will eliminate the mosquito eggs, larvae and reduce the number of mosquitoes present in these areas.
- Cover water containers tightly so that mosquitoes can’t get in to lay eggs.
Aedes Aegypti mosquito
- Aedes aegypti mosquitoes most commonly bite at dusk and dawn, indoors, in shady areas, or when the weather is cloudy.
- The mosquitoes prefer to breed in areas of stagnant water, such as flower vases, uncovered barrels, buckets, water coolers and discarded tires.
- Some of the dangerous areas are wet floors and toilet tanks, as they allow the mosquitoes to breed in the residence.
- Although the lifespan of an adult Aedes aegypti is 2-4 weeks depending on conditions, the eggs can be viable for over a year in dry state. This allows the mosquito to reappear after a cold winter or dry spell.
Dengue fever symptoms
- Symptoms usually develop within 3-14 days after being exposed to the dengue virus (also known as incubation period). The average incubation period is around 4-7 days.
- Symptoms of dengue are:
- Sudden-onset fever
- Headache (typically located behind the eyes)
- Muscle and joint pain
- Rash
- Chills (shivering)
- Facial flushing
- Loss of appetite
- Sore throat
- Abnormal bleeding such as nosebleeds, bleeding gums and/or blood in your urine









Good Job keep it up Sumit
ReplyDelete